Chile SEO Success Story: Reaching the Top 1 with Smart Use of Canonicals and Hreflangs
- Niche: iGaming
- GEO: Chile
- Website Type: Monobrand (Single Main Page)
Announcement:
In this case study, we show how using a network of 20 drop domains + a main site led to achieving top rankings in the iGaming niche in Chile. Over the course of 4 weeks, each domain received between 300 and 1,000 backlinks per week (depending on the intermediate performance of the site).
For the most effective sites, we additionally launched sitewide
links and direct
traffic. Thanks to the correct implementation of canonical and
hreflang tags, most of the link equity was safely passed to the main domain.
The full strategy, technical details, results, and key takeaways are outlined below.
Week 1: Setup & Planning
A client approached us with a website that had unstable rankings (around positions 40–50) and was already receiving backlinks from forums, blogs, and a small number of guest posts. The goal was to push the site into the top 3 for the main high-volume keywords and secure that position.
To achieve the desired results, we decided to build a network of supporting sites to strengthen the main domain using canonical tags for link consolidation.
To fully understand what was done, we recommend reviewing this case study alongside the spreadsheet: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/16P5kfmmhzazkFkWkAL85i59ZuLLWAmzyambFelcb2dE/edit?gid=0#gid=0 .
The spreadsheet contains a detailed log of all tasks completed throughout the project. Domain names are not disclosed due to NDA restrictions.
Main Project Promotion
A four-week strategy was developed and launched to boost the client's main project through backlinks and traffic.
Week 1:
- 300 blog backlinks (100% non-anchor).
Week 2:
- 500 blog-post backlinks (80% non-anchor);
- Additional traffic for 4 days, 20,000 visitors per day.
Week 3:
- 1,000 blog-post backlinks (60% non-anchor);
- 5 sitewide links (100% anchor);
- Additional traffic for 7 days, 20,000 visitors per day.
Week 4:
- 1,000 blog-post backlinks (60% non-anchor);
- 5 sitewide links (100% anchor);
- Additional traffic for 7 days, 40,000 visitors per day.
Selecting Drop(Expired/Aged) Domains
In the top 10 search results for our target keywords, 90% of the websites were over 5 years old. For our client’s relatively new project, it was virtually impossible to break into this niche using only standard White Hat SEO methods without additional interventions.
To strengthen the main website, we decided to use drop domains — in order to transfer accumulated trust and link equity from older sites to the new resource.
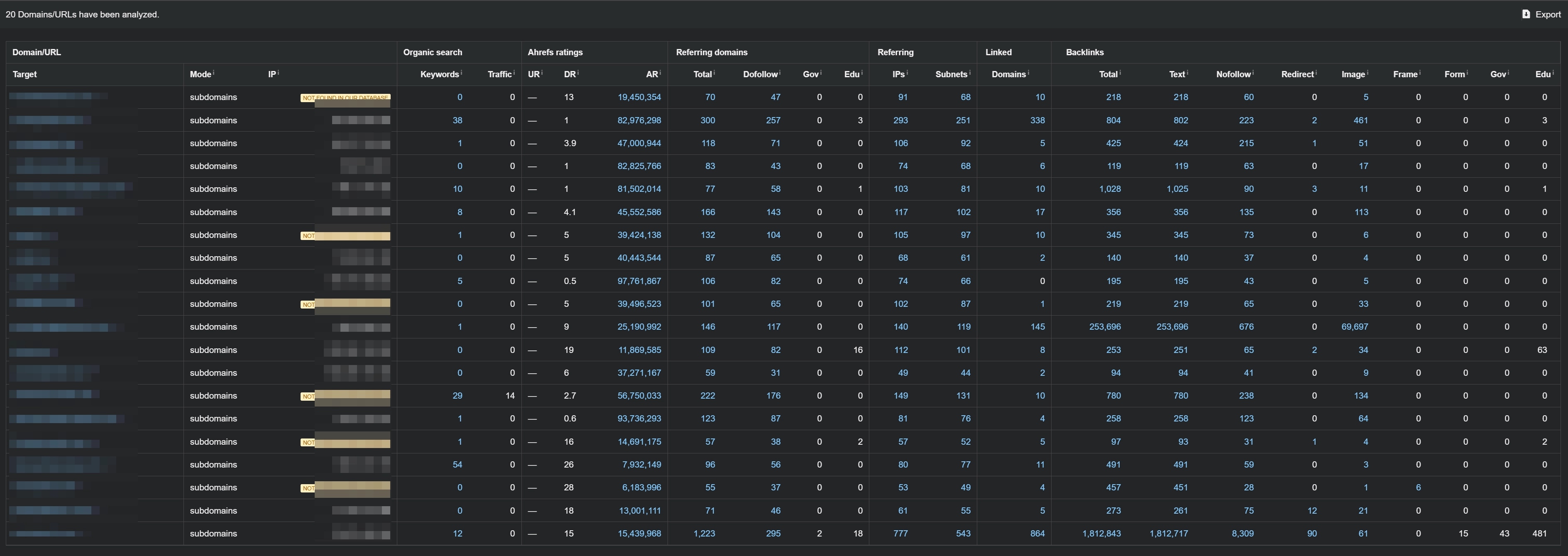
We purchased 20 drop domains. The domains covered a variety of topics (blog-style resources, corporate websites), but none were directly related to gambling.
Key selection criteria:
- Presence of historical traffic (from Google);
- A clean backlink profile with no spam or unnatural spikes;
- A natural cause for traffic loss (e.g., site abandonment), rather than penalties or merges. Based on our experience: if Google previously trusted a domain and visibility was lost due to natural reasons, it will often restore rankings for a new project built on that domain — as long as the transition is handled correctly.
Technical Details
The sites were launched without any prior drop domain preparation:
- No restoration of old content from web archives;
- No gradual thematic transition was implemented;
- A new template and unique content were used from the start.
The websites were built using simple HTML templates, without any CMS or admin panel — all content was uploaded directly via the server.
AI tools were used to generate both templates and images, and the results were then reviewed by a technical specialist.
Technical Parameters:
- Google PageSpeed Insights score: 95;
- TTFB (Time to First Byte): 20 ms for users in Chile;
- All 404 pages with incoming backlinks were redirected to the homepage, where new relevant content was placed.
All sites were blocked from indexation by backlink analysis bots (Ahrefs, Majestic, etc.) at the Cloudflare level (using WAF Custom Rules), preventing competitors from analyzing the backlink profile or detecting links from the drop domains to the main site.
Fake content was implemented for all sites — only the original Googlebot sees the actual content (verified via RDNS lookup), while other bots and users see topic-relevant but conversion-optimized material.
This was done in order to:
- Confuse competitors;
- Protect site structure and content from being copied;
- Hide the technical implementation details of the promotion strategy.
Content Preparation
Each site was handed over to copywriters to produce around 1,500 words of content for the homepage. This was high-quality AI-generated content, edited by a human and localized to match the brand and regional specifics.
Mini Guide: How We Created Unique Content for Drop Domains
▼
The goal was to quickly generate accurate, unique, and localized content for dozens of drop sites — without triggering filters or duplicate content issues. Here's how we did it:
- Extracting Real Content from the SERPs
We didn’t ask AI to generate content from scratch. Before generation, we scraped all content from the top 30 sites for our target keywords. This dataset was then fed to the AI model as the foundation for the articles. It gave us precise data on casinos: minimum deposits, bonuses, payment methods, providers.
Without this step, AI often fabricates key facts — and gets them wrong 9 out of 10 times. We eliminated this issue at the source.
- Variation = Uniqueness
Each article was generated in a separate AI thread and did not overlap with others. Every article used a unique prompt with specific instructions such as:
– Who is the article written from (casino owner, player, reviewer...);
– What tone the brand should be described in;
– The article’s purpose (to inform, to review, to criticize).
Each article also had a different keyword density.Result: None of the sites had more than 10% content similarity — even when covering the same topic.
- Content Quality Control
After generation, each text went through:
– Manual review for local tone and logic;
– AI detection check (Originality.AI, Copyleaks);
– SEO review: headlines, keywords, metadata.We didn’t fight filters after publishing — we crafted the content so filters had no reason to trigger in the first place.
- Scale Without a Trace
We launched 20 sites simultaneously, but due to prompt variation, Google perceived them as independent sites with legitimate editorial footprints.
Indexing
To accelerate indexing for all 20 domains, we used a combination of additional traffic and manual pinging via Google Search Console. Important: a separate Google account was used for each site.
Traffic was driven to each site for a period of 2 days, at a rate of 20,000 users per day.
Results After Week 1
By the end of the first week, all 20 drop domains were successfully indexed. Out of those:
- 6 sites — did not receive any rankings;
- 5 sites — had unstable rankings beyond the top 50;
- 9 sites — achieved rankings in the top 30 to top 100 range and held them steadily without major drops or spikes.
As for the main project: there were no significant changes in rankings — the site remained in the 40–50 range for the main target keywords.
A Brief Philosophical Note: The SEO Anomaly Approach
There’s one crucial aspect of SEO that most people ignore or simply don’t realize.
Imagine a typical website without an SEO specialist. What needs to happen for it to start gaining new backlinks? First of all, the site needs traffic. If there’s no traffic — who would be linking to it? Who would share its content?
From Google’s perspective, it doesn’t make sense when a site with zero traffic suddenly gets 1,000 new backlinks in a month. That kind of situation is only possible through SEO intervention — and it’s easy to detect.
That’s why our promotion strategy is based on the principle of logical behavior: backlinks appear in parallel with traffic, and traffic grows alongside site updates. This creates a natural-looking pattern for the search engine.
Week 2: Strategy Adjustment Based on Results
After analyzing the results from Week 1, we categorized all sites based on their search engine rankings into three groups:
- Weak — sites that didn’t achieve any rankings
- Mid-tier — sites with unstable rankings
- Top-performing — sites with relatively stable positions within the top 100
Promotion
Weak Sites
- Promotion was stopped;
- If a site didn’t achieve any rankings, it likely indicates hidden issues (penalties, poor historical profile, etc.). Further investment is not justified.
Mid-tier Sites
- 500 blog-post backlinks (90% non-anchor);
- Direct traffic: 4 days with 20,000 visitors per day (every other day).
Top-performing Sites
- 1,000 blog-post backlinks (90% non-anchor);
- Direct traffic: 4 days with 20,000 visitors per day (every other day).
Main Project
- Promotion continued according to the original plan, with no changes.
Content Updates
Logically speaking, we assume that on websites without SEO specialists, new backlinks typically appear only when something changes or is added — in other words, when there’s a newsworthy update that sparks interest or buzz.
To maintain the organic nature of our promotion, we added a new content block to the homepage of each site scheduled for link building that week.
These blocks varied in content depending on the specific site:
- Some featured information about new bonuses;
- Others included updates about new slot providers or changes in the game selection.
This gave a logical reason for the appearance of new mentions and backlinks, making the activity appear natural both to search engines and external observers.
Results
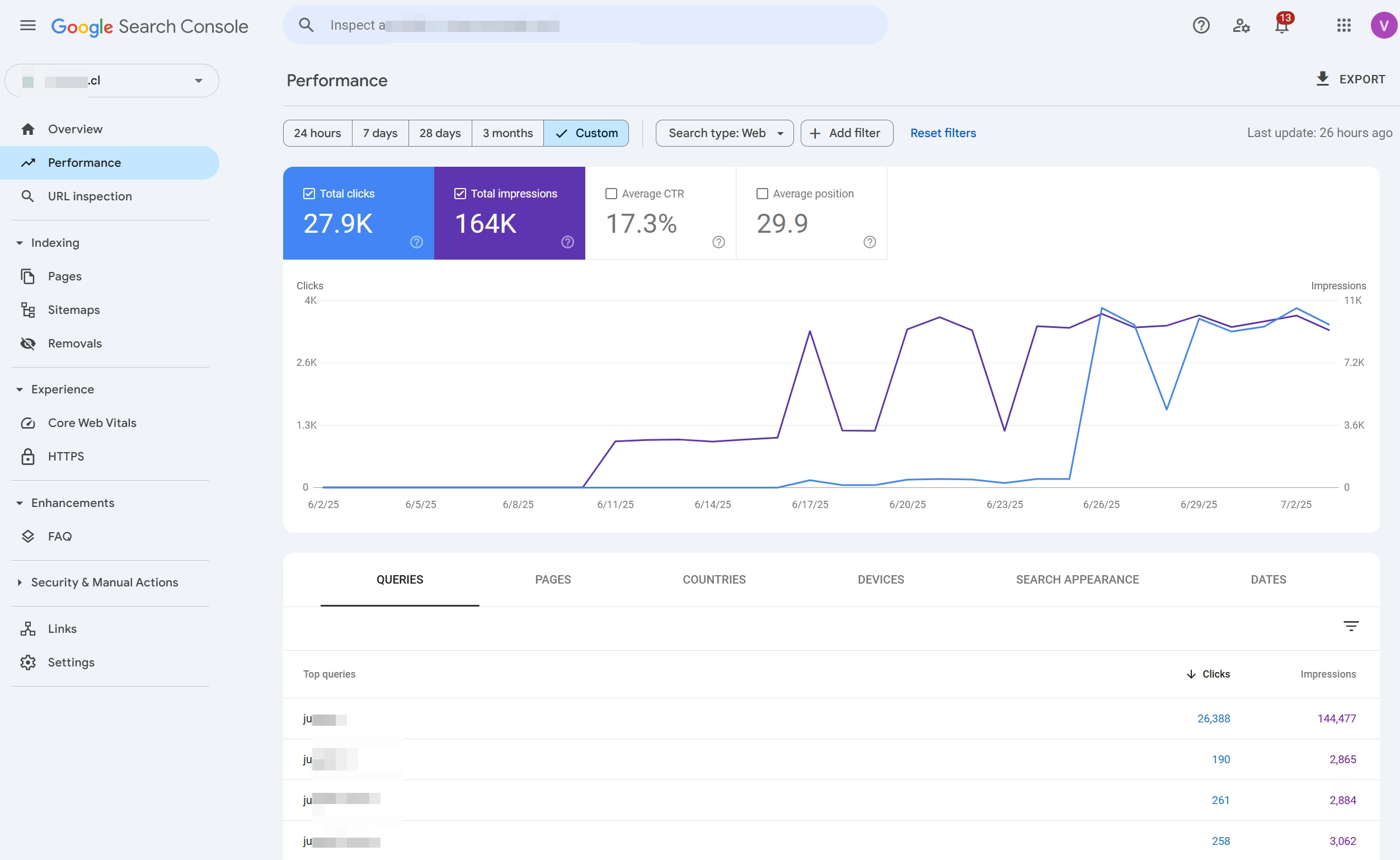
This week, we introduced direct traffic to the main project for the first time, which led to a noticeable boost in rankings — the site climbed to position 20 for its main keywords and started appearing for many new queries in the visibility report.
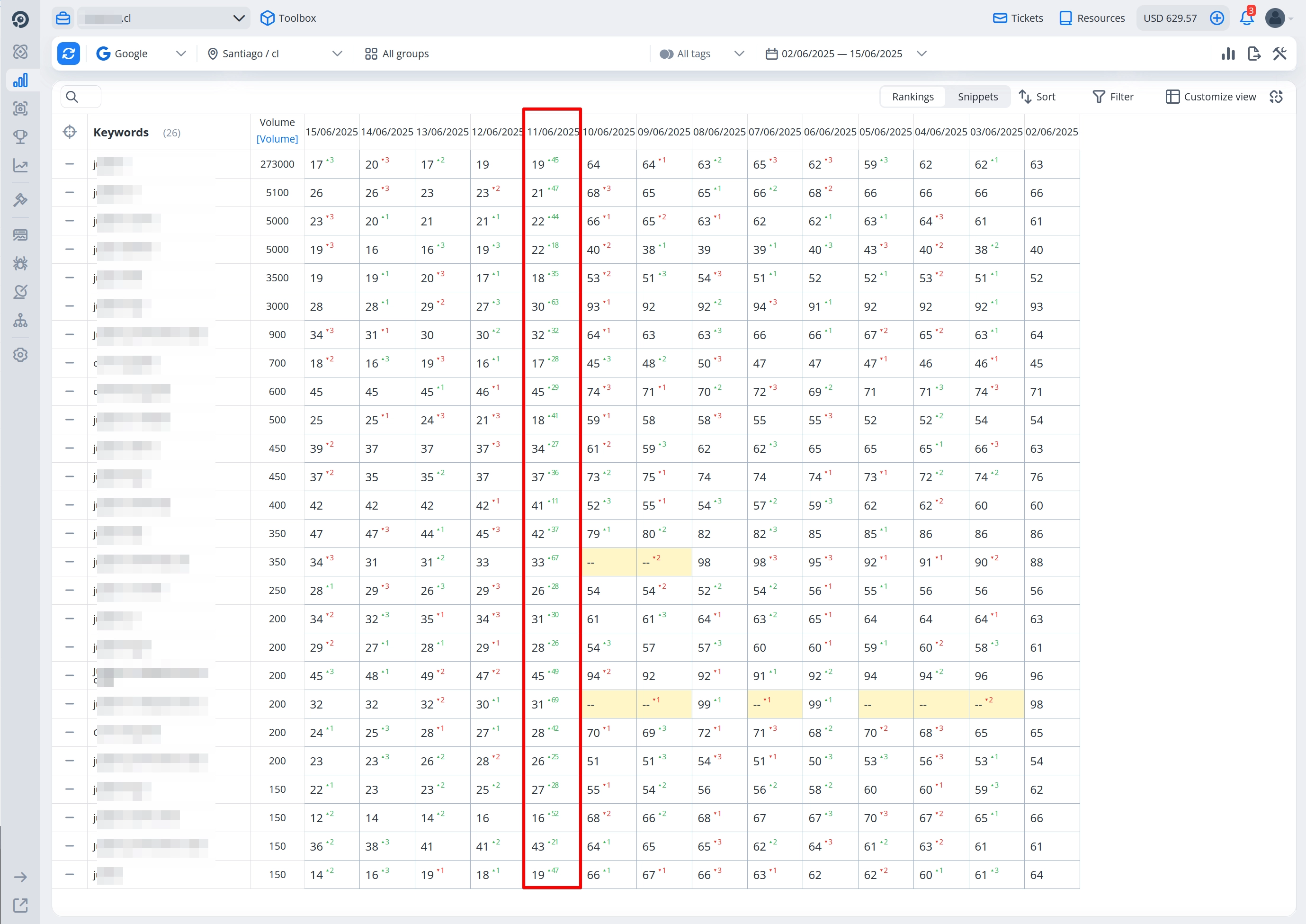
Regarding the drop domain network:
Mid-tier sites:
- 2 sites — completely lost their rankings;
- 1 site — continued to show unstable performance;
- 2 sites — stabilized in rankings → moved to the Top-performing category.
Weak sites:
- 1 site — unexpectedly reached the top 20 but only for a few hours; later, it disappeared entirely;
- The rest — no change.
Top-performing sites:
- 3 sites — started fluctuating heavily in rankings → downgraded to Mid-tier;
- The rest — showed slight but consistent growth.
We observed a range of outcomes across the drop domains, but thanks to the large-scale launch (20 sites), we were able to accurately assess the effectiveness of the approach.
If we had launched only 5 drop domains, the variability would have been too high — making it nearly impossible to draw meaningful conclusions about the strategy’s effectiveness.
Week 3: Executing the Initial Plan
Promotion Strategy
In Week 3, we continued with the updated approach, taking into account the current performance of each group of sites.
Weak Sites
- Promotion stopped;
- No changes were made, as these drop domains showed no potential even after previous efforts.
Mid-tier Sites
- 500 blog-post backlinks (70% non-anchor);
- Direct traffic: 4 days with 20,000 visitors per day (every other day).
Top-performing Sites
- 1,000 blog-post backlinks (70% non-anchor);
- 5 sitewide links (100% anchor);
- Direct traffic: 7 days with 20,000 visitors per day.
Main Project
- Promotion continued as planned, following the base strategy.
Implementing the Canonical Link Strategy
In Week 3, we identified the 8 most effective drop domains that showed stable rankings. After additional link building and traffic boosts, it was time to execute the core part of the strategy — linking the drop domains to the main site using canonical tags.
We did not merge all sites at once, but instead divided them into two groups to enable a gradual rollout and maintain better control over the results.
Implementation Scheme:
- A full replica of the main site — including the same design and content — was deployed on each selected drop domain.
-
The sites were interlinked using
hreflangtagds to define regional targeting, along withcanonicaltags:- For the drop domains — Spanish language + other regions
(
es-MX, etc.); - For the main site — Spanish language + Chile (
es-CL); - From all sites — a
canonicalpointing to the main site.
- For the drop domains — Spanish language + other regions
(
HTML Implementation Code:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://*******.cl/">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-CL" href="https://*******.cl/">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-MX" href="https://rus**************.com/">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-ES" href="https://cro*****.io/">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-AR" href="https://cns*******.com/">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-BR" href="https://sec************.cl/">
This approach allowed us to legally and effectively transfer authority from the drop domains to the main site via:
- Canonicals — to send a direct signal to Google indicating which URL is the primary one;
- Hreflang — to make all sites appear as parts of a multi-regional project.
Results After Canonical Integration
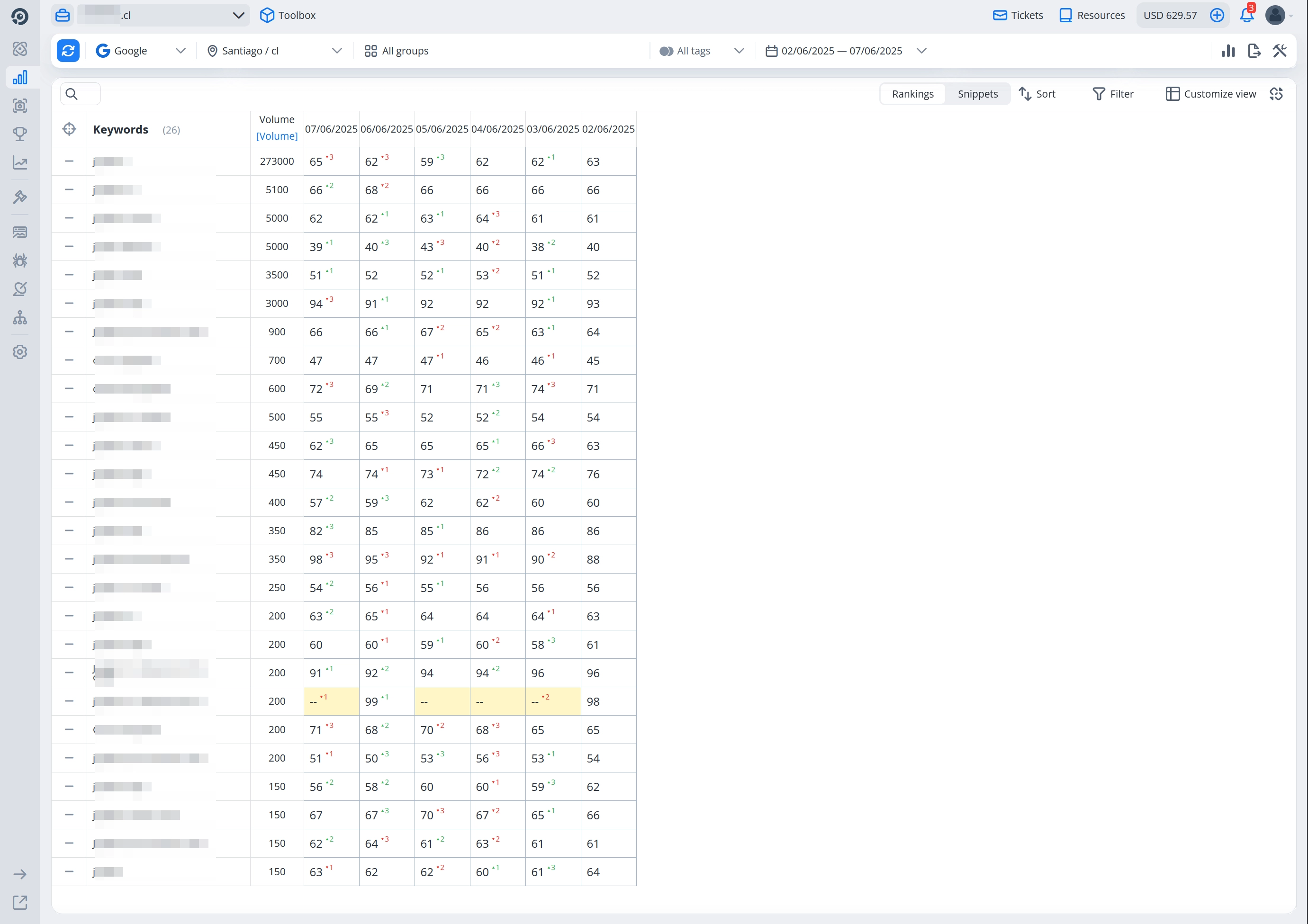
Just one day after implementing the canonical merge, we observed a significant boost in rankings on the main domain:
- 10th position for the main high-volume keyword
- Many medium-volume keywords entered the top 10
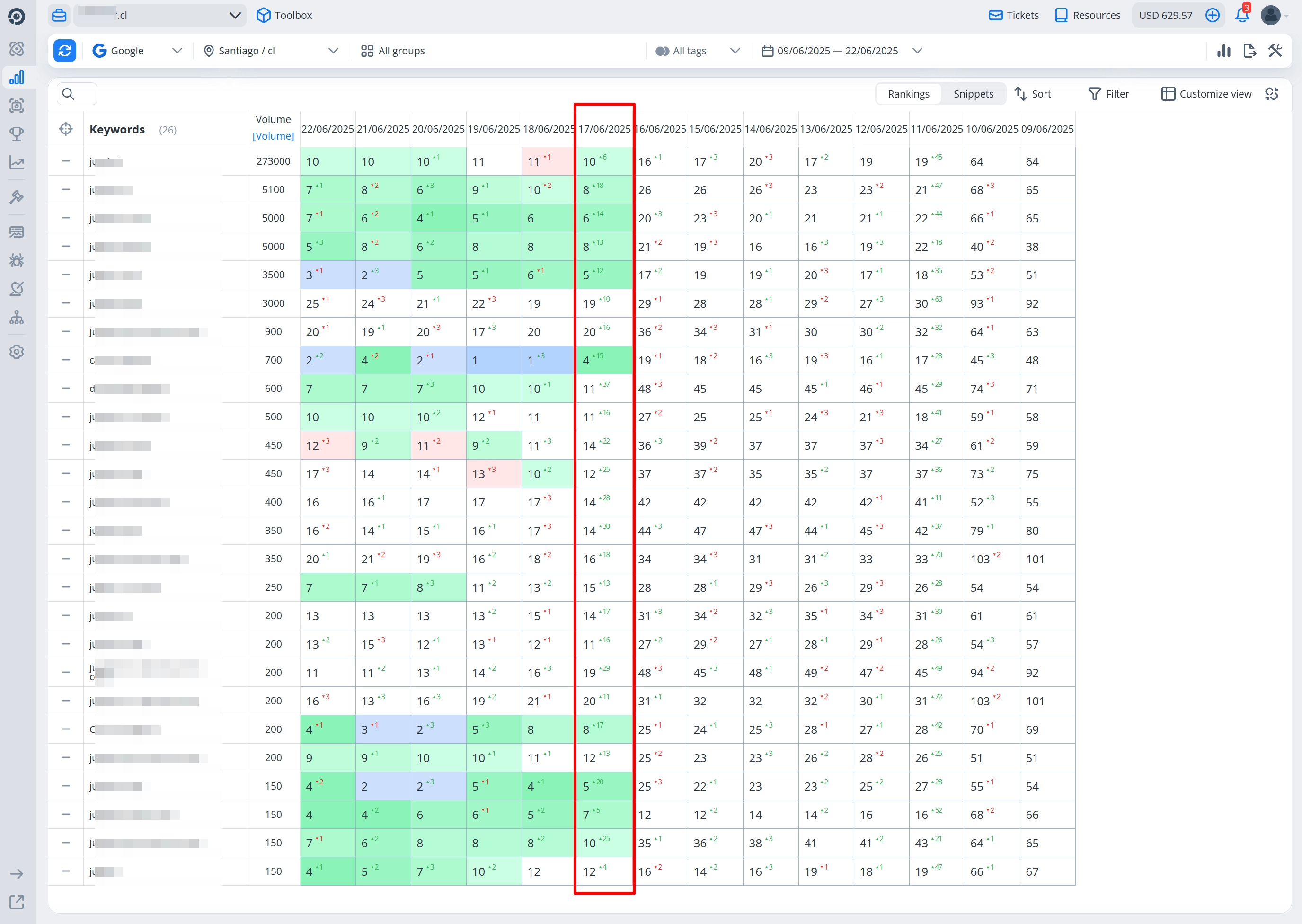
The success was driven by 4 drop domains that were linked — all 4 successfully passed authority to the main site. Fast canonical integration was made possible thanks to continuous traffic and properly implemented canonical tags.
Quick Guide: How to Check if a Site is Canonically Attached or Redirected
▼
Even without access to Search Console, you can check if a site is canonically linked or redirected to another domain. This is useful for competitor analysis.
How to check:
- Use the following URL:
- Replace
domain-to-check.comwith the domain you want to inspect. - If the site is linked to another, Google will display that relationship on the results page.
https://www.google.com/search?q=About+https://domain-to-check.com/&tbm=ilp&cs=1&ctx=atrExample:
For the domain yolcutiyatro.com:
https://www.google.com/search?q=About+https://yolcutiyatro.com/&tbm=ilp&cs=1&ctx=atr
On the results page, you'll see that the site is canonically linked or redirected to
altuncayrestoran.com — that domain is the one actually ranking.
Results from Other Sites:
- The 4 drop domains used for canonical linking lost all of their rankings — this is the expected outcome after passing authority via canonical tags.
- The remaining drop domains that were not linked did not show any significant changes in visibility.
Week 4: The Final Stage
Promotion
In Week 4, we continued promotion based on the performance of each site group:
Weak Sites
- No promotion.
Mid-tier Sites
- 500 blog-post links (70% non-anchor);
- 4 days of traffic, 20,000 users per day (every other day).
Top-performing Sites
- 1,000 blog-post links (70% non-anchor);
- 5 sitewide (100% anchor);
- 7 days of traffic, 20,000 users per day.
Main Project
- Promotion continued according to the original plan.
Top-performing Sites Already Linked to the Main Project
- Promotion was not stopped in order to avoid signaling a loss of value to Google.
- Reduced intensity:
- 300 blog-post links (70% non-anchor);
- 7 days of traffic, 20,000 users per day.
To fully leverage the link equity from the Mid-tier drop domains and avoid wasting their value, we decided together with the client to merge them (using 301 redirect) into our Top-performing sites.
In contrast, we chose not to link the Weak sites, as there was a risk of transferring penalties or filters — which likely explained why they weren’t ranking in the first place.
Finalizing Canonical Integrations
At the beginning of the week, we added the remaining 4 Top-performing sites to the Hreflang linking scheme.
HTML Implementation Code:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://*******.cl/">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-CL" href="https://*******.cl/">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-MX" href="https://rus**************.com/">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-ES" href="https://cro*****.io/">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-AR" href="https://cns*******.com/">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-BR" href="https://sec************.cl/">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-PL" href="https://hai*********.com/">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-SE" href="https://pac*****.cl/">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-MD" href="https://jcr**.org/">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-RU" href="href="https://des*************.cl/">
Results After Linking 4 More Sites
On the 3rd day after adding the new drop domains, we saw a boost in both rankings and traffic — reaching position 1 for the main keyword, and many medium-volume keywords entering the top 1–3.
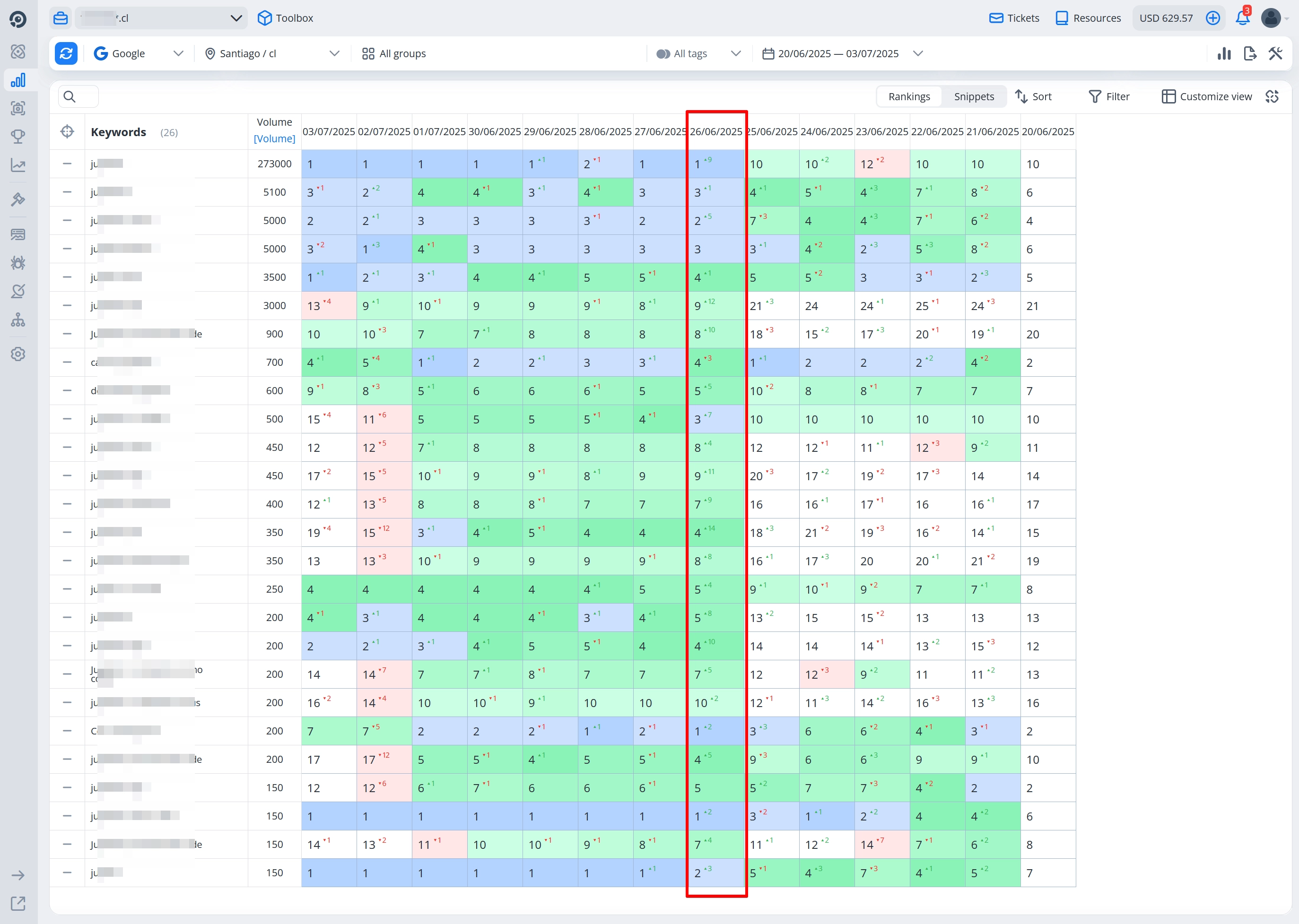
Summary
As of now, the site ranks #1 for its main target keyword. Occasionally, it drops to top 2, as we are competing with a project that has consistently held a top-3 position for over 4 years and has a very strong backlink profile.
Ongoing Promotion:
- Main site: we continue building traffic and backlinks.
- Supporting sites (drop domains): we continue adding links and traffic, but at lower volumes — just enough to keep the network “alive” and avoid devaluation by Google.
Financial Note:
Since this is a client-owned project and the client chose not to disclose financial data, we are unable to provide a full public P&L statement.
That said, we can confirm that this project was costly to support, but it has already paid off: the client has commissioned the promotion of two more sites using the same strategy.